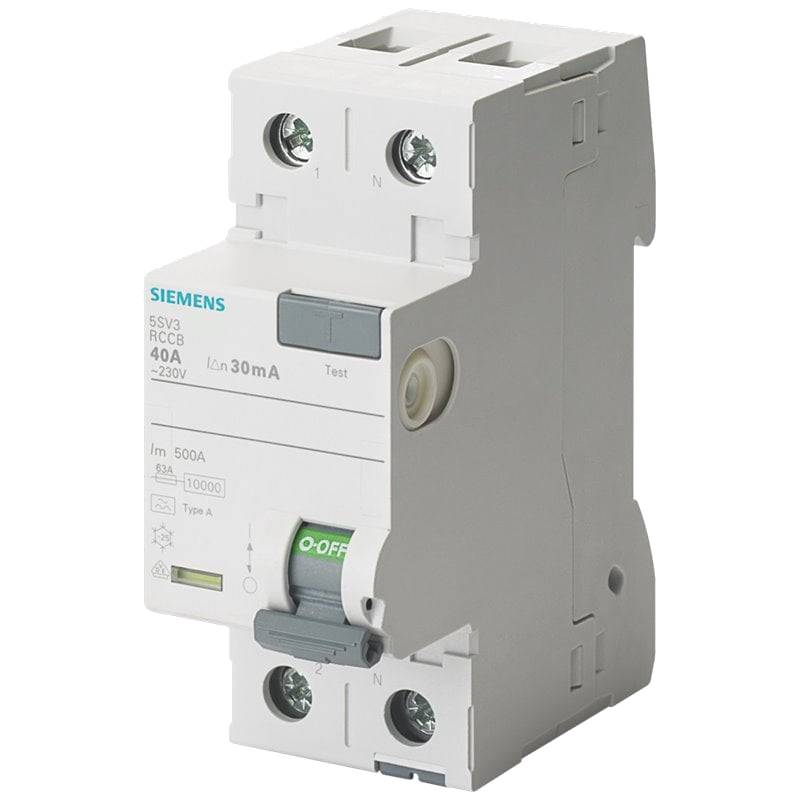
The Siemens 5SV3621-4 Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is a robust two-pole, 16-ampere device with a 300mA sensitivity, engineered for reliable overcurrent and short-circuit protection in diverse electrical installations. Its compact design, high breaking capacity, and swift tripping mechanism ensure enhanced safety and operational continuity. This MCB stands out for its robust construction, adherence to stringent international safety standards, and seamless integration into various switchboard systems, making it a preferred choice for demanding industrial and commercial applications.
Product Specifications
| Feature | Specification |
| :---------------------- | :------------------------------------------- |
| Product Type | Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) |
| Pole Configuration | 2-Pole (Double Pole) |
| Rated Current (In) | 16 A |
| Rated Sensitivity (IΔn) | 300 mA (0.3 A) |
| Breaking Capacity (Icn) | 6 kA (kA - kiloamperes) |
| Voltage Rating (Ue) | 230/400 V AC |
| Tripping Characteristic | Type B or C (common, specific model may vary) |
| Frequency | 50/60 Hz |
| Terminal Type | Screw Terminals |
| Mounting Type | DIN Rail (35 mm) |
| Protection Class | IP20 (body), IP40 (enclosure) |
| Standards Compliance | IEC/EN 60898-1, IEC/EN 61009-1 |
Core Features & Market Positioning
The Siemens 5SV3621-4 MCB excels with its precise and reliable tripping characteristics, safeguarding electrical circuits from damaging overloads and short circuits. Its 300mA residual current sensitivity is particularly vital for applications requiring enhanced protection against indirect contact, such as in domestic, commercial, and certain industrial settings where increased risk of electric shock exists. Siemens' reputation for quality and durability positions this MCB as a dependable component within the protection device market, offering peace of mind and extended service life even under rigorous operating conditions. The robust breaking capacity of 6 kA ensures it can safely interrupt fault currents, preventing catastrophic damage to the electrical system.
Key Application Scenarios
This 2-pole, 16A, 300mA MCB is ideally suited for protecting individual circuits within residential distribution boards, commercial buildings, and light industrial facilities. It is frequently employed for branch circuit protection of lighting, socket outlets, and small appliances where a residual current tripping threshold of 300mA is mandated or recommended for safety. Its application extends to areas with higher humidity or proximity to water, such as workshops or utility rooms, where the risk of earth faults is elevated. The 2-pole design allows for simultaneous disconnection of both live and neutral conductors, crucial for complete isolation and maintenance.
Practical System Integration Guidance
Installation of the Siemens 5SV3621-4 MCB on a standard 35mm DIN rail is straightforward, requiring no specialized tools. Ensure the main power supply is de-energized before commencing any wiring. Connect the incoming live and neutral conductors to the designated terminals, typically marked with 'L' and 'N' respectively, adhering to local wiring regulations and the polarity indicated on the device. The outgoing circuit conductors are connected to the lower terminals. For optimal performance and safety, it is crucial to use correctly sized conductors that match the MCB's 16A rating and ensure all connections are mechanically sound and electrically secure to prevent overheating.
Operation and Risk Mitigation
The Siemens 5SV3621-4 MCB operates by continuously monitoring the current flow through both live and neutral conductors. If an imbalance greater than 300mA is detected, indicative of a fault current to earth, the device will instantaneously trip, interrupting the circuit. This rapid response is critical for preventing electric shock hazards and mitigating fire risks associated with electrical faults. Should the MCB trip unexpectedly, common causes include insulation breakdown in connected appliances, short circuits, or overloading beyond the 16A capacity. Inspect all connected equipment and wiring for visible damage or signs of overheating. Avoid repeatedly resetting a tripping breaker without identifying and rectifying the underlying fault.
Scalability & Long-Term Value
While a single MCB unit provides protection for a specific circuit, its value lies in its compatibility with the broader Siemens SENTRON system and established electrical infrastructure. The modular design of Siemens protection devices allows for easy replacement or addition of MCBs as electrical system requirements evolve. Integration with modern smart home or building automation systems can be achieved through compatible residual current devices (RCDs) or specialized monitoring modules that work in conjunction with MCBs, enabling remote status monitoring and control, thus contributing to the long-term digital transformation of electrical installations.
*
FAQs
1. What is the primary function of the Siemens 5SV3621-4 MCB?
This MCB provides overcurrent and short-circuit protection. It also offers residual current detection for enhanced safety against earth faults.
It acts as a crucial safety device in electrical distribution systems. The 300mA sensitivity helps prevent electric shocks by rapidly disconnecting power.
Its robust design ensures reliable operation across various environmental conditions found in industrial settings.
2. What does "2P 16A 300mA" signify on the Siemens 5SV3621-4?
"2P" indicates it is a two-pole breaker, switching both live and neutral. "16A" is its rated current capacity, meaning it protects circuits up to 16 amperes.
"300mA" is the residual current sensitivity, the fault current level that triggers the device to trip. This threshold is important for personal protection.
Together, these specifications define the MCB's core protective capabilities and application scope for specific electrical circuits.
3. Can the Siemens 5SV3621-4 be used in residential applications?
Yes, this MCB is highly suitable for residential use, particularly for branch circuits. Its 300mA sensitivity offers a good level of protection against indirect contact.
It ensures safety for circuits powering outlets, lighting, and appliances in homes and apartments. Compliance with relevant safety standards is key.
Proper installation by a qualified electrician is always recommended to guarantee optimal performance and safety in any home electrical system.
4. What is the breaking capacity of this MCB, and why is it important?
The Siemens 5SV3621-4 has a breaking capacity of 6 kA. This indicates the maximum fault current it can safely interrupt without sustaining damage.
A higher breaking capacity is crucial for installations where significant fault currents are possible, preventing explosive failures. It ensures circuit integrity during severe short circuits.
This specification is a critical safety parameter, determining the MCB's suitability for different levels of electrical system fault risk.
5. How does the 300mA residual current sensitivity protect users?
The 300mA threshold detects leakage currents that could flow through a person to earth. Such currents can be dangerous and cause severe injury or electrocution.
When this imbalance is detected, the MCB trips almost instantaneously, cutting off the power supply. This rapid disconnection minimizes the duration and severity of electric shock.
This feature significantly enhances personal safety, especially in environments where contact with conductive surfaces or wet conditions is more likely.
6. What are the implications of the 2-pole design for installation and safety?
A 2-pole MCB disconnects both the live and neutral conductors simultaneously. This ensures complete isolation of the circuit from the power supply for maintenance.
It prevents the neutral conductor from remaining live if the live conductor is disconnected separately. This is a vital safety measure for preventing shock hazards.
For circuits requiring full isolation, such as those controlled by a switch disconnect or in specific building codes, 2-pole protection is often mandatory.
7. Where is the Siemens 5SV3621-4 typically installed within an electrical system?
This MCB is commonly installed in main distribution boards or sub-distribution panels. It protects individual outgoing circuits from the main power supply.
It forms part of the protective device lineup, installed on a standard 35mm DIN rail for secure and organized mounting. Correct wiring is essential.
Its position ensures that a fault on one circuit does not affect others, allowing for targeted troubleshooting and maintenance.
8. What types of tripping characteristics are available for this MCB?
While specific models vary, MCBs like the 5SV3621-4 are often available with Type B or Type C tripping characteristics. Type B is for lower inrush currents, Type C for higher ones.
Type B MCBs typically trip at 3-5 times the rated current, suitable for resistive loads. Type C MCBs trip at 5-10 times the rated current, for inductive loads.
Selecting the correct tripping characteristic is important to avoid nuisance tripping while ensuring adequate protection against short circuits.
9. Does this MCB comply with international safety standards?
Yes, the Siemens 5SV3621-4 Miniature Circuit Breaker complies with key international standards. These include IEC/EN 60898-1 and IEC/EN 61009-1.
These certifications ensure the device has undergone rigorous testing for performance, safety, and reliability. Adherence to standards is critical for electrical safety.
Using products that meet these global benchmarks guarantees a level of quality and protection expected in modern electrical installations.
10. How does this MCB integrate with modern IIoT or smart building solutions?
Direct integration is limited, but it can be part of a system monitored by smart devices. It serves as the foundational protection for circuits.
Smart residual current monitoring units or gateways can be used alongside MCBs to provide data on trip events and status. This enables remote diagnostics.
While not inherently "smart," its reliable operation and compatibility with Siemens' broader product ecosystem facilitate its inclusion in increasingly digitized electrical infrastructure.